Analysis of deoxyribonuclease activity by conjugation-free fluorescence polarisation in sub-nanolitre droplets†
Abstract
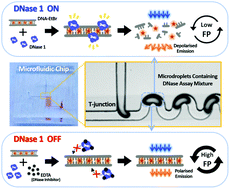
We report the analysis of deoxyribonuclease (DNase) activity by conjugation-free fluorescence polarisation in a droplet-based microfluidic chip. DNase is a DNA cleaving enzyme and its activity is important in the maintenance of normal cellular functions. Alterations in DNase activity have been implicated as the cause of various cancers and autoimmune diseases. To date, various methods for the analysis of DNase activity have been reported. However, they are not cost effective due to the requirement of large sample volumes and the need for the conjugation of fluorescent dyes. In this study, we have used ethidium bromide (EtBr), a DNA intercalating reagent, as a fluorescent reporter without any prior conjugation or modification of DNA. Degradation of DNA by DNase 1 was monitored at a steady state by making changes in the fluorescence polarisation of EtBr in droplets with a volume of 330 picolitre at a 40 hertz frequency under visible light. Using this technique, we successfully determined the half-maximal inhibitory concentration (IC50) of ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA) for the inhibition of DNase 1 activity to be 1.56 ± 0.91 mM.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...