Effects of surface treatments on trapping with DC insulator-based dielectrophoresis†
Abstract
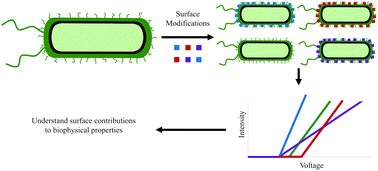
A central challenge in measuring the biophysical properties of cells with electrokinetic approaches is the assignment of these biophysical properties to specific biological characteristics. Changes in the electrokinetic behavior of cells may come from mutations, altered gene expression levels, post-translation modifications, or environmental effects. Here we assess the electrokinetic behavior of chemically surface-modified bacterial cells in order to gain insight into the biophysical properties that are specifically affected by changes in surface chemistry. Using E. coli as a scaffold, an amine coupling reaction was used to covalently attach glycine, spermine, bovine serum albumin (protein), or 7-amino-4-methyl-3-coumarinylacetic acid (fluorescent dye) to the free carboxylic acid groups on the surface of the cells. These populations, along with unlabeled control cells, were subject to electrokinetic and dielectrophoretic measurements to quantify any changes in the biophysical properties upon alteration. The properties associated with each electrokinetic force are discussed relative to the specific reactant used. We conclude that relatively modest and superficial changes to cell surfaces can cause measurable changes in their biophysical properties.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...
