A novel N/Au co-doped carbon dot probe for continuous detection of silicate and phosphate by resonance Rayleigh scattering†
Abstract
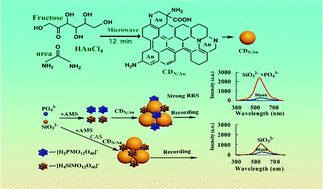
Co-doped carbon dots are new multifunctional carbon nanomaterials. Their fast preparation and new analytical applications such as in continuous detection and resonance Rayleigh scattering (RRS) probes are of interest to people. Herein, the N/Au co-doped carbon dots (CDN/Au) were prepared quickly by a microwave synthesis method using fructose as the carbon source and urea and HAuCl4 as dopants, and it exhibited an excellent RRS effect at 555 nm. Based on both silicate (SiO32−) and phosphate (PO43−) reacting with ammonium molybdate to form silicomolybdate heteropoly acid (SiMo) and phosphomolybdate heteropoly acid (PMo), PMo decomposed by the addition of citric acid, and SiMo/PMo combined with CDN/Au to show good RRS analytical properties, and a new strategy was developed to detect SiO32− and PO43− by the CDN/Au probes continuously. With the increase of SiO32− (PO43−), SiMo (PMo) reacted with CDN/Au probes to form more big particles which resulted in the RRS intensity enhancement at 555 nm, and had a good linear relationship with the SiO32− (PO43−) concentration in the range of 1.11 μg L−1–19.98 μg L−1, with detection limits of 0.3 μg L−1 SiO32− and 0.3 μg L−1 PO43−. Accordingly, a new RRS method was established for continuous detection of SiO32− and PO43− using CDN/Au as the probe.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...