In situ monitoring of electrochemical reactions through CNT-assisted paper cell mass spectrometry†
Abstract
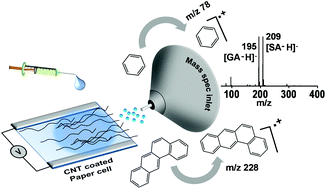
A novel method of coupling electrochemistry (EC) with mass spectrometry (MS) is illustrated with a paper-based electrochemical cell supported by carbon nanotubes (CNTs). The electrochemically formed ions, created at appropriate electrochemical potentials, are ejected into the gas phase from the modified paper, without the application of additional potential. The electrochemical cell was fabricated by using a rectangular CNT-coated Whatman 42 filter paper with printed electrodes, using silver paste. This was used for studying the electrochemical conversion of thiols to disulfides, and the functionalization of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs), which involve S–S and C–C bond formations, respectively. We also demonstrate the versatility of the set-up by utilizing it for the detection of radical cations of metallocenes, monitoring the oxidation of sulfides through the detection of reactive intermediates, and the detection of radical cations of PAHs, all of which occur at specific applied potentials. Finally, the applicability of this technique for qualitative and quantitative analyses of environmentally relevant molecules has been demonstrated by studying the electrochemical oxidation of glucose (Glu) to gluconic acid (GlcA) and saccharic acid (SacA).


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...