Raman spectroscopic screening of high and low molecular weight fractions of human serum†
Abstract
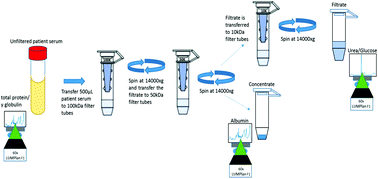
This study explores the suitability of Raman spectroscopy as a bioanalytical tool, when coupled with ultra-filtration and multivariate analysis, to detect imbalances in both high molecular weight (total protein content, γ globulins and albumin) and low molecular weight (urea and glucose) fractions of the same samples of human patient serum, in the native liquid form. Ultracentrifugation was employed to separate and concentrate the high and low molecular weight fractions of the serum. Initially, aqueous solutions of the respective molecular species, covering physiologically relevant concentration ranges, were analysed to optimise the measurement protocols. An adapted Extended Multiplicative Signal Correction (EMSC) algorithm was applied to raw spectra to remove water background signal and spectral interferents (β-carotene). Using a validated partial least squares regression modelling method, R2 values, Root Mean Square Error of Cross Validation (RMSECV) and standard deviations were established for the quantification of γ globulin, total protein, albumin, urea and glucose content of the patient serum samples. The study demonstrates that Raman spectroscopy in the liquid form is a viable alternative and/or adjunct to current clinical practice for the parallel analysis of high and low molecular weight fractions, and simultaneous analysis of multiple analytes in the low molecular weight fraction, of human serum for diagnostic applications.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...