Enhanced selectivity of target gas molecules through a minimal array of gas sensors based on nanoparticle-decorated SWCNTs†
Abstract
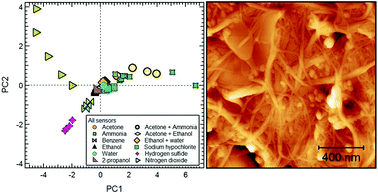
An array of five sensors, based on carbon nanotubes (CNT) functionalized with nanoparticles of Au, TiO2, ITO, and Si has been fabricated and exposed to a selected series of target gas molecules (NH3, NO2, H2S, H2O, benzene, ethanol, acetone, 2-propanol, sodium hypochlorite, and several combinations of two gases). The results of principal component analysis (PCA) of the experimental data show that this array of sensors is able to detect different target gas and to discriminate each molecule in the 2D PCA parameters space. In particular, the possibility to include in the array a humidity sensor significantly increases the capability to discriminate the response to volatile organic compounds (VOCs), even though VOCs usually react with CNTs less than NO2 or NH3. This leads to an improvement in selectivity that could meet the requirements for gas detection applications in the field of environmental monitoring and breathomics, where sensors are exposed to a variety of different molecules and where the humidity can severely affect the overall response of the sensor. Finally, we demonstrate that the ability to test multiple sensors simultaneously can reveal a specific sensor sensitivity, addressing the best functionalization choice to improve the response of new sensors based on decorated CNT layers. In particular, our study shows the better capability of the ITO-decorated sensor to detect H2S and benzene.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...