Nanogold hybrid silica gel and its 1-octadecanethiol self-assembled modified composite as a stationary phase for liquid chromatography†
Abstract
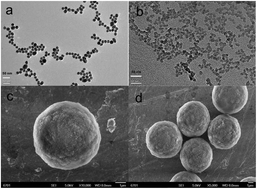
Au nanoparticle-hybridized silica (Au@sil) spheres were synthesized in one step as a liquid chromatographic stationary phase for the first time. The hybridized stationary phase showed good separation performances in reversed-phase liquid chromatography (RPLC) and hydrophilic interaction liquid chromatography even without bonding with any organic groups. Compared with the bare silica stationary phase, the Au@sil stationary phase showed better separation performance under the same conditions in RPLC and HILIC modes. The effects of acetonitrile content, buffer concentration, and the pH of the mobile phase on analyte retention were further investigated. The results showed that the Au@sil stationary phase had a complex retention mechanism of electrostatic and partitioning interactions. By comparing Au solution (solAu) with different proportion volumes in silica sol, the optimum hybridized stationary phase was found to comprise 33 vol% solAu. Au@sil was further modified with 1-octadecanethiol by self-assembly and used to separate alkylbenzenes and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons by RPLC. The separation efficiency of the 1-octadecanethiol self-assembled modified Au@sil (C18-Au@sil) column was much better than that of Au@sil. Overall, the successful hybridization of Au nanoparticles provided a new method to prepare a stationary phase in a simple and environmentally friendly way.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...