Microfluidic array surface ion-imprinted monolithic capillary microextraction chip on-line hyphenated with ICP-MS for the high throughput analysis of gadolinium in human body fluids†
Abstract
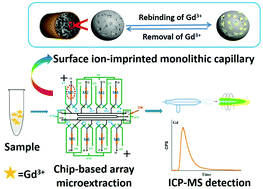
A novel method by hyphenating chip-based array ion-imprinted monolithic microextraction with inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (ICP-MS) was proposed for the online analysis of trace Gd in biological samples in this work. The poly(γ-methacryloxypropyltrimethoxysilane@Gd3+-surface ion-imprinted polymer) [poly(γ-MAPS@Gd3+-SIIP)] monolithic capillary was prepared via in situ polymerization on the vinyl-modified surface of poly(γ-MAPS) using Eu3+ as the mimic template. The prepared ion-imprinted monolithic capillary possessed higher selectivity and adsorption capacity to Gd3+ than the non-imprinted monolithic capillary. Eight poly(γ-MAPS@Gd3+-SIIP) monolithic capillaries were embedded in the channels of a microfluidic chip to fabricate a chip-based array microextraction device. Factors affecting the selectivity of the prepared ion-imprinted monolithic capillary including imprinted time and the composition of the prepolymerization solution, and extraction conditions for the fabricated chip-based array ion-imprinted monolithic capillary microextraction platform were optimized. A sample throughput of 18 h−1 was achieved along with a low detection limit of 1.27 ng L−1 for Gd3+. The proposed chip-based array poly(γ-MAPS@Gd3+-SIIP) monolithic microextraction-ICP-MS method was used for the analysis of trace Gd in human urine and serum, and the recovery for spiking experiments was in the range of 88.1–96.7%. The developed integrated analysis platform possesses good interference resistance, high automation, high sensitivity and low consumption of the sample/agent, which makes it very suitable for the analysis of trace elements in complicated biological samples.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...