Deep learning for FTIR histology: leveraging spatial and spectral features with convolutional neural networks
Abstract
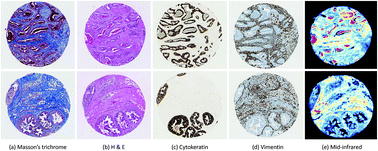
Current methods for cancer detection rely on tissue biopsy, chemical labeling/staining, and examination of the tissue by a pathologist. Though these methods continue to remain the gold standard, they are non-quantitative and susceptible to human error. Fourier transform infrared (FTIR) spectroscopic imaging has shown potential as a quantitative alternative to traditional histology. However, identification of histological components requires reliable classification based on molecular spectra, which are susceptible to artifacts introduced by noise and scattering. Several tissue types, particularly in heterogeneous tissue regions, tend to confound traditional classification methods. Convolutional neural networks (CNNs) are the current state-of-the-art in image classification, providing the ability to learn spatial characteristics of images. In this paper, we demonstrate that CNNs with architectures designed to process both spectral and spatial information can significantly improve classifier performance over per-pixel spectral classification. We report classification results after applying CNNs to data from tissue microarrays (TMAs) to identify six major cellular and acellular constituents of tissue, namely adipocytes, blood, collagen, epithelium, necrosis, and myofibroblasts. Experimental results show that the use of spatial information in addition to the spectral information brings significant improvements in the classifier performance and allows classification of cellular subtypes, such as adipocytes, that exhibit minimal chemical information but have distinct spatial characteristics. This work demonstrates the application and efficiency of deep learning algorithms in improving the diagnostic techniques in clinical and research activities related to cancer.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...