Green, fast, and large-scale synthesis of highly fluorescent Au nanoclusters for Cu2+ detection and temperature sensing†
Abstract
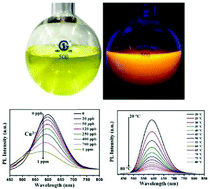
Gold nanoclusters have attracted widespread attention because of their unique optical and physical properties. However, traditional synthesis methods are complicated and require additional reducing agents, while the yield is often very low. Such resource and time-consuming synthesis processes limit their further application. Herein, a rapid sonochemical route is used to synthesize fluorescent Au nanoclusters in large quantities using glutathione (GSH) both as a capping and reducing agent. These Au nanoclusters are synthesized quickly (∼40 min) due to the presence of ultrasonic waves, and show orange red photoluminescence (Em = 598 nm), small size (∼2 nm) and good dispersion in aqueous solution. Moreover, GSH, as a protecting agent on the surface of resultant Au nanoclusters, has many functional groups including carboxyl and amino groups because of which the nanoclusters show high photo-, storage-, metal- and pH-stability. A stable Au nanoclusters-based nano-sensor is designed for highly sensitive and selective label-free detection of Cu2+ with a low limit of detection of 7 ppb (based on S/N = 3). The fluorescent probe can be used in versatile nanothermometry devices, because their photoluminescence intensity correlates strongly with temperature and varies considerably over a wide temperature range (20–80 °C). Therefore, the novel fluorescent sensing probe has great application prospects in Cu2+ detection and temperature sensing.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...