Absolute two-point quantification of proteins using dimethylated proteotypic peptides†
Abstract
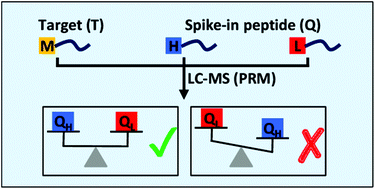
Absolute targeted proteomics typically employs known amounts of synthetic stable isotopically labeled peptides which are mixed with the analyte and analysed by LC-MS to determine the concentration of proteins. In order to obtain more data, we evaluated the use of two different stable isotopes of the same peptide as spike-in for absolute quantification. For this purpose, peptide labeling by reductive amination was applied, which is a mild reaction for dimethylation of amine groups with very high yield. Three different forms can be generated with e.g., light and heavy labels for spike-in peptides, and medium label for endogenous peptides. The method was studied with peptides of apolipoprotein A-I, apolipoprotein B-100, and leucine-rich alpha-2-glycoprotein without and with serum. In serum, the endogenous protein concentrations were measured across four orders of magnitude by the two-point quantification method. Less than 20% of coefficient of variation (CV) values and strong correlation with R2 of 0.99 across three analytical replicates was observed. Most importantly, the two-point quantification method allows an internal quality control of the spike-in peptide as strong deviations in ratios calculated between the first and second reference indicate a methodical error. Because of the significant lower costs than synthetically stable isotopically labeled peptides, this approach might be particularly interesting for the absolute quantification of multiple proteins.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...