Fluorescence hyperspectral imaging for live monitoring of multiple spheroids in microfluidic chips†
Abstract
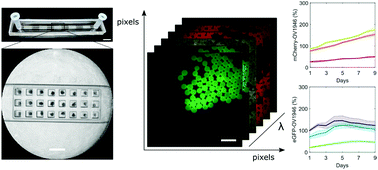
Tumor spheroids represent a realistic 3D in vitro cancer model because they provide a missing link between monolayer cell culture and live tissues. While microfluidic chips can easily form and assay thousands of spheroids simultaneously, few commercial instruments are available to analyze this massive amount of data. Available techniques to measure spheroid response to external stimuli, such as confocal imaging and flow cytometry, are either not appropriate for 3D cultures, or destructive. We designed a wide-field hyperspectral imaging system to analyze multiple spheroids trapped in a microfluidic chip in a single acquisition. The system and its fluorescence quantification algorithm were assessed using liquid phantoms mimicking spheroid optical properties. Spectral unmixing was tested on three overlapping spectral entities. Hyperspectral images of co-culture spheroids expressing two fluorophores were compared with confocal microscopy and spheroid growth was measured over time. The system can spectrally analyze multiple fluorescent markers simultaneously and allows multiple time-points assays, providing a fast and versatile solution for analyzing lab on a chip devices.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...