Ligand-displacement-based two-photon fluorogenic probe for visualizing mercapto biomolecules in live cells, Drosophila brains and zebrafish†
Abstract
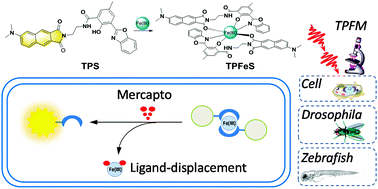
Investigating the change in expression level of mercapto biomolecules (GSH/Cys/Hcy) necessitates a rapid detection method for a series of physiological and pathological processes. Herein, we present a ligand-displacement-based two-photon fluorogenic probe based on an Fe(III) complex, TPFeS, which is a GSH/Cys/Hcy rapid detection fluorogenic probe for in vitro analysis and live cell/tissue/in vivo imaging. The “in situ” probe is non-fluorescent and was prepared from a 1 : 2 ratio of Fe(III) and TPS, a novel two-photon (TP) fluorophore with excellent one-photon (OP) and TP properties under physiological conditions, as a fluorescent ligand. This probe shows a rapid and remarkable fluorescence restoration (OFF–ON) property due to the ligand-displacement reaction of mercapto biomolecules in a recyclable manner in vitro. A significant two-photon action cross-section, good selectivity for biothiols, low cytotoxicity, and insensitivity to pH over the biologically relevant pH range allowed the direct visualization of mercapto biomolecules at different levels between normal/drug-treated live cells, as well as in Drosophila brain tissues/zebrafish based on the use of two-photon fluorescence microscopy.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...