Fluorometric detection of EGFR exon 19 deletion mutation in lung cancer cells using graphene oxide†
Abstract
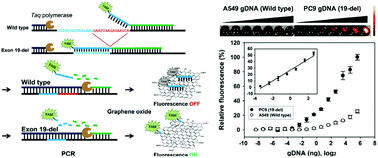
Mutations in epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) are known as biomarkers that cause non-small cell lung cancer. Particularly, approximately 45% of non-small cell lung cancer patients possess a deletion in exon 19 of the EGFR gene. A less invasive method for detecting the EGFR mutation is required; thus, we developed a simple polymerase chain reaction (PCR)-based method for detecting EGFR exon 19 deletion by using a quencher-free fluorescent probe DNA and graphene oxide (GO). In the presence of the exon 19 deletion mutation, the fluorophore-labeled DNA probe was designed to be fully complementary to the mutant sequences. The fully annealed DNA probe was degraded by the 5′ to 3′ exonuclease activity of Taq DNA polymerase during PCR, releasing the fluorophore from the probe DNA. In contrast, a wild-type gene only allowed partial annealing of the probe DNA to the amplicon because of the absence of the deletion sequences, with Taq polymerase digestion releasing unannealed fragments of probe DNA. When GO was added to each reaction solution, starkly different fluorescence signals were obtained; enhanced fluorescence was observed because of the released fluorophore from the probe DNA that was not adsorbed onto GO, whereas fluorescence was quenched when the fragmented single-stranded probe DNA was readily adsorbed onto GO. Our method enabled the detection of as low as 49 pg of EGFR exon 19 deletion DNA with a detection limit of 0.1% when the mutant genomic DNA was mixed with wild-type DNA.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Analyst Recent HOT articles


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...