Highly stable SERS pH nanoprobes produced by co-solvent controlled AuNP aggregation†
Abstract
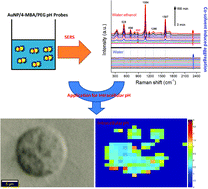
Production of gold nanoparticle (AuNP) surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy (SERS) nanoprobes requires replicable aggregation to produce multimers with high signal intensity. Herein, we illustrate a novel, yet simple, approach to produce SERS nanoprobes through control of co-solvent composition. AuNP multimers were produced by mixing AuNP monomers in water : ethanol co-solvent for variable periods of time. By varying the water : ethanol ratio and the amount of 4-mercaptobenzoic acid (4-MBA) present, the aggregation rate can be systematically controlled. Thiolated poly(ethylene glycol) was then added to halt the aggregation process and provide steric stability. This approach was used to produce pH nanoprobes with excellent colloidal stability in high ionic strength environments and in complex samples. The pH probe exhibits broad pH sensitivity over the range 6–11 and we calculate that a single AuNP dimer in a 35 fL volume is sufficient to generate a detectable SERS signal. As a proof-of-concept, the probes were used to detect the intracellular pH of human prostate cancer cells (PC-3). The internalized probes exhibit a strong 4-MBA signal without any interfering bands from either the cells or the culture media and produce exceptionally detailed pH maps. pH maps obtained from 19 xy surface scans and 14 yz depth scans exhibit highly consistent intracellular pH in the range of 5 to 7, thus indicating the greater reliability and reproducibility of our pH probes compared with other probes previously reported in the literature. Our water : ethanol co-solvent production process is fast, simple, and efficient. Adjustment of solvent composition may become a powerful way to produce SERS tags or nanoprobes in the future.
- This article is part of the themed collections: Analyst Recent Open Access Articles and Surface-enhanced Raman scattering


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...