A magnetic nanoparticle-based aptasensor for selective and sensitive determination of lysozyme with strongly scattering silver nanoparticles†
Abstract
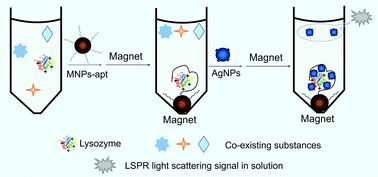
Qualitative and quantitative determination of lysozyme concentrations in urine and serum with high selectivity and sensitivity is important for diagnosing the progression of several diseases. In this report, we devised an improved method for specifically detecting lysozyme by combining magnetic nanoparticles (for separation and enrichment), an aptamer (for selective binding of lysozyme) and strongly scattering silver nanoparticles (AgNPs, for detection by light scattering, but also providing another level of selectivity due to their electrostatic binding with lysozyme). In this system, 0.4–30 nM lysozyme could be simply detected owing to the decreased light scattering of AgNPs in solution after magnetic separation, with a detection limit of 100 pM. In addition, lysozyme was also able to be semi-quantified by using the dark-field light scattering images of AgNPs after enrichment by the MNP–apt–lysozyme complex. Moreover, this design shows great promise for the robust and reliable detection of lysozyme in real samples, with a recovery rate ranging from 98.6% to 101.3% in human serum samples. Therefore, this assay provided robust measurements with good specificity, sensitivity, and tolerance of changes in the sample matrix. We expect that this MNP-based aptasensor may find utility in the accurate diagnosis of lysozyme-related diseases.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...