Synthesis of “amphiphilic” carbon dots and their application for the analysis of iodine species (I2, I− and IO3−) in highly saline water†
Abstract
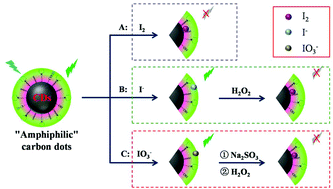
“Amphiphilic” carbon dots (A-CDs) with a strong green fluorescence emission were synthesized by a simple and green method at room temperature. The characterization demonstrated that the synthesized A-CDs have both hydrophilic and hydrophobic properties and could be dispersed well in aqueous and organic solutions. As a fluorescent probe, the fluorescence of A-CDs could be obviously quenched in the presence of iodine (I2) and the quenching rate is proportional to the concentration of I2. Therefore, the A-CDs could be used as fluorophores for the detection of I2 with higher selectivity and sensitivity, and the linear working range for the I2 sensor is 80 nM–10 μM with a detection limit of 3.5 nM (S/N = 3). More interesting is that IO3− and I− could be transformed to I2 with different sample treatment processes, therefore, the I2 sensor based on A-CDs could also be used for the analysis of iodine species (I2, I− and IO3−) in samples. The possible mechanism has also been discussed in this work, and the high selectivity response to I2 can be attributed to the amphiphilic properties of A-CDs, which bring I2 closer to A-CDs and quench their fluorescence. The proposed I2 sensor has been successfully used for the analysis of iodine species in highly saline water, and the satisfactory results of detection and analysis of iodine species in samples demonstrate that the developed I2 sensor based on A-CDs has potential application in the fields of environment and clinical medicine.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...