Ratiometric fluorescence sensor arrays based on quantum dots for detection of proteins†
Abstract
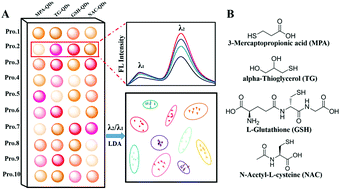
Optical cross-reactive sensor arrays have recently been demonstrated as a powerful tool for high-throughput protein analysis. Nevertheless, applying this technology to protein detection is complicated by many external factors, such as the interfering substances, the background noise, and sample environmental changes in the biological matrix. Herein we demonstrate that a ratiometric fluorescence sensor array based on quantum dots can be employed to circumvent these limitations. Several intrinsic dual-emitting Mn-doped quantum dots capped with different organic functional groups were designed as sensing elements. Distinct and reproducible response patterns against the ratiometric sensor array were obtained from ten proteins in a buffer of different pH (pH 5.7, 7.4, and 8.3) and spiked into human urine. Linear discrimination analysis of the response patterns showed successful differentiation of the analytes at concentrations as low as 50 nM with high identification accuracy. Furthermore, this sensor system also enables the detection of these eight proteins (at 500 nM) in human urine without any treatment. The ratiometric fluorescence change from quantum dots for analysis of proteins can eliminate effectively the signal interference from the pH value change and the fluorescent background in human urine. The present study will open a new avenue to improve the discrimination ability of sensor arrays.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...