An immobilization free DNAzyme based electrochemical biosensor for lead determination
Abstract
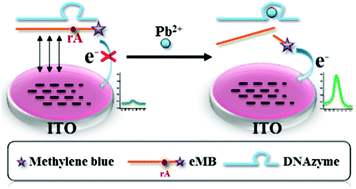
DNAzyme based electrochemical biosensors have the characteristics of high sensitivity and selectivity, but traditional DNAzyme based electrochemical biosensors need the immobilization of DNAzyme on the electrode surface first, and the procedures are time consuming and tedious, which limit their real application. In this study, a simple but sensitive immobilization free DNAzyme based electrochemical biosensor has been proposed and lead has been chosen as a model target because of the severe effects of lead toxicity. The different diffusivity and electrostatic repulsion between long and short DNA on the negatively charged ITO electrode can be used to discriminate the short and long DNA. Lead dependent DNAzyme was hybridized with its substrate (which was modified with methylene blue at the 3′ terminal) beforehand. Since the DNAzyme/substrate complex contains a large negative charge, it cannot diffuse easily to the negatively charged ITO electrode surface and little electrochemical signal has been detected. The presence of lead would trigger the cleavage of the DNAzyme/substrate complex and cause the release of a methylene blue-labeled short-oligonucleotide into the solution. The methylene blue-labeled short-oligonucleotide can diffuse easily to the surface of the negatively charged ITO electrode and results in the enhanced electrochemical response being detected. Each lead can cleave a lot of DNAzyme/substrate complex to realize signal amplification. The enhanced electrochemical signal has a linear relationship with the Pb2+ concentration in the range of 0.05–1 μM with a detection limit of 0.018 μM (S/N = 3). The proposed biosensor has been applied to detect Pb2+ in water samples with satisfactory results.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...