Amplification-free in situ KRAS point mutation detection at 60 copies per mL in urine in a background of 1000-fold wild type†
Abstract
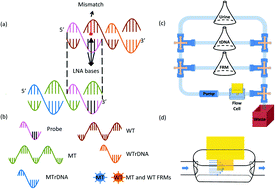
We have examined the in situ detection of a single-nucleotide KRAS mutation in urine using a (Pb(Mg1/3Nb2/3)O3)0.65(PbTiO3)0.35 (PMN-PT) piezoelectric plate sensor (PEPS) coated with a 17-nucleotide (nt) locked nucleic acid (LNA) probe DNA complementary to the KRAS mutation. To enhance the in situ mutant (MT) DNA detection specificity against the wild type (WT), detection was carried out in a flow with a flow rate of 4 mL min−1 and at 63 °C with the PEPS vertically situated at the center of the flow in which both the temperature and the flow impingement force discriminated the wild type. Under such conditions, PEPS was shown to specifically detect KRAS MT in situ with 60 copies per mL analytical sensitivity in a background of clinically-relevant 1000-fold more WT in 30 min without DNA isolation, amplification, or labeling. For validation, this detection was followed with detection in a mixture of blue MT fluorescent reporter microspheres (FRMs) (MT FRMs) that bound to only the captured MT and orange WT FRMs that bound to only the captured WT. Microscopic examinations showed that the captured blue MT FRMs still outnumbered the orange WT FRMs by a factor of 4 to 1 even though WT was 1000-fold of MT in urine. Finally, multiplexed specific mutation detection was demonstrated using a 6-PEPS array each with a probe DNA targeting one of the 6 codon-12 KRAS mutations.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...