A novel fluorescence assay for inorganic pyrophosphatase based on modulated aggregation of graphene quantum dots†
Abstract
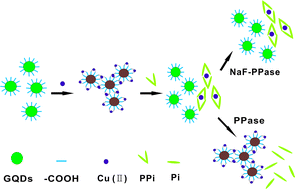
A simple and highly sensitive fluorometric method has been developed for inorganic pyrophosphatase (PPase) activity detection based on the disaggregation and aggregation of graphene quantum dots (GQDs). Copper ions can trigger the severe aggregation of GQDs with rich carboxyl groups, which results in effective fluorescence quenching. While, with the addition of pyrophosphate (PPi), the quenched fluorescence is effectively recovered owing to the strong interaction between PPi and Cu2+. Furthermore, under the catalytic hydrolysis of PPase, the complex of PPi–Cu2+–PPi is rapidly disassembled, and the fluorescence is re-quenched. This method is highly sensitive and selective for PPase detection, with a linear correlation between the fluorescence intensity and the PPase concentration in the range from 1 to 200 mU mL−1 with a detection limit down to 1 mU mL−1 (S/N = 3). Additionally, the inhibition effect of NaF on the PPase activity is also studied. Thus, the proposed method may hold a potential application in the diagnosis of PPase-related diseases and screening of PPase inhibitors, to evaluate the function and inhibition of PPase in biological systems.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...