Gold nanoparticle-catalyzed uranine reduction for signal amplification in fluorescent assays for melamine and aflatoxin B1†
Abstract
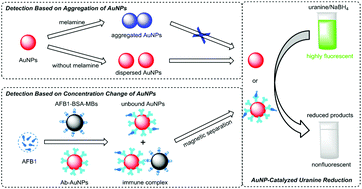
A multifunctional fluorescence platform has been constructed based on gold nanoparticle (AuNP)-catalyzed uranine reduction. The catalytic reduction of uranine was conducted in aqueous solution using AuNPs as nanocatalyst and sodium borohydride as reducing reagent, which was monitored by fluorescence and UV-vis spectroscopy. The reaction rate was highly dependent on the concentration, size and dispersion state of AuNPs. When AuNPs aggregated, their catalytic ability decreased, and thereby a label-free fluorescent assay was developed for the detection of melamine, which can be used for melamine determination in milk. In addition, a fluorescent immunoassay for aflatoxin B1 (AFB1) was established using the catalytic reaction for signal amplification based on target-induced concentration change of AuNPs, where AFB1-BSA-coated magnetic beads and anti-AFB1 antibody-conjugated AuNPs were employed as capture and signal probe, respectively. The detection can be accomplished in 1 h and acceptable recoveries in spiked maize samples were achieved. The developed fluorescence system is simple, sensitive and specific, which could be used for the detection of a wide range of analytes.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...