Removable interpenetrating network enables highly-responsive 2-D photonic crystal hydrogel sensors
Abstract
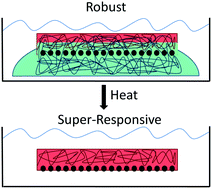
Responsive hydrogels functionalized with molecular recognition agents can undergo large volume changes upon interactions with specific chemical species. These responsive hydrogels can function as chemical sensing materials if the hydrogel volumes are monitored by using devices such as photonic crystals (PhC). An important criterion of merit is the responsiveness of these sensing hydrogels. Generally, hydrogel responsiveness is inversely proportional to the hydrogel crosslink density because the elastic constants scale with the crosslink density. The responsivities of these hydrogel sensors dramatically increase as their hydrogel crosslinker concentrations decrease. Unfortunately, the resulting highly responsive hydrogels become fragile at low crosslink densities, and are hard to fabricate and utilize. To temporarily increase the mechanical strengths of these highly responsive hydrogels we developed a method to incorporate a removable reinforcing interpenetrating hydrogel network. We demonstrate the utility of this approach by incorporating an interpenetrating PVA hydrogel within a weak, low crosslinked pH sensitive hydrogel through a freeze–thaw process. These interpenetrating PVA hydrogels are indefinitely stable at room temperature, but easily dissolved on transient heating to 70 °C. The pH sensing hydrogel response is unaffected by this incorporation and subsequent dissolution of the interpenetrating PVA hydrogel. These sacrificial hydrogels enable the fabrication and utilization of highly responsive hydrogel sensing materials.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...