Enzyme-free and label-free signal amplification for monitoring endonuclease activity and inhibition via hybridization chain reaction†
Abstract
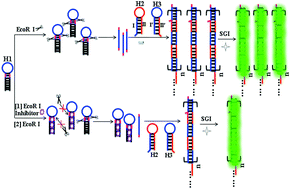
A label-free and enzyme-free amplification protocol has been proposed for studying endonuclease activity and inhibition on the basis of the enzyme-digested product triggered hybridization chain reaction (HCR). Three hairpin oligonucleotides were designed as probes which could not open or hybridize with each other at room temperature until the initiator DNA was released by specific enzymatic cleavage in the presence of endonuclease to trigger the hybridization chain reaction. SYBR Green I was chosen as a signal probe which intercalated into the grooves of the nicked double DNA polymer, generating a substantially apparent increase in fluorescence intensity. Once the activity of endonuclease is inhibited by enzyme inhibitors, the efficiency of HCR will be greatly decreased. Therefore, screening of endonuclease inhibitors can be achieved effectively as well as the assay of endonuclease activity. Meanwhile, the assay of endonuclease activity and inhibition achieves a better performance as compared to the previous reports. Importantly, it is a more universal method that can be simply used to study activity and inhibition of other endonucleases by changing the specific recognition site. So, the protocol was proved to be a sensitive and cost-effective approach for studying endonuclease activity and inhibition, and as such, it is promising for broad potential application in various biological reactions.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...