Electrokinetic preconcentration of particles and cells in microfluidic reservoirs†
Abstract
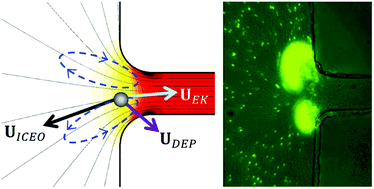
Preconcentrating samples of dilute particles or cells to a detectable level is required in many chemical, environmental and biomedical applications. A variety of force fields have thus far been demonstrated to capture and accumulate particles and cells in microfluidic devices, which, however, all take place within the region of microchannels and may potentially cause channel clogging. This work presents a new method for the electrokinetic preconcentration of 1 μm-diameter polystyrene particles and E. coli cells in a very-low-conductivity medium inside a microfluidic reservoir. The entire microchannel can hence be saved for a post-concentration analysis. This method exploits the strong recirculating flows of induced-charge electroosmosis to concentrate particles and cells near the corners of the reservoir–microchannel interface. Positive dielectrophoresis is found to also play a role when small microchannels are used at high electric fields. Such an in-reservoir electrokinetic preconcentration method can be easily implemented in a parallel mode to increase the flow throughput, which may potentially be used to preconcentrate bacterial pathogens in water.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...