β-Cyclodextrin functionalised gold nanoclusters as luminescence probes for the ultrasensitive detection of dopamine†
Abstract
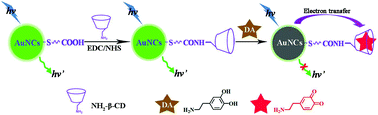
A novel luminescence probe based on mono-6-amino-β-cyclodextrin (NH2-β-CD) functionalised gold nanoclusters (β-CD-AuNC) was designed for dopamine (DA) detection. The NH2-β-CD molecules were conjugated onto the surface of 11-mercaptoundecanoic acid capped AuNCs (11-MUA-AuNC) via a carbodiimide coupling reaction. The integrity of the β-CD cavities was preserved on the surface of AuNCs and they retained their capability for molecular DA host–guest recognition. DA could be captured by the β-CD cavities to form an inclusion complex in which the oxidised DA could quench the fluorescence of the β-CD-AuNC probe by electron transfer. The probe could be used to quantify DA in the range of 5–1000 nM with a detection limit of 2 nM. This sensitivity was 1–2 orders of magnitude higher than that in previously reported methods. Interference by both ascorbic acid (AA) and uric acid (UA) was not observed. Therefore, the β-CD-AuNC probe could be directly used to determine the DA content in biological samples without further separation. This strategy was successfully applied to a DA assay in spiked human serum samples and it exhibited remarkable accuracy, sensitivity and selectivity.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...