A new method for wavelength interval selection that intelligently optimizes the locations, widths and combinations of the intervals
Abstract
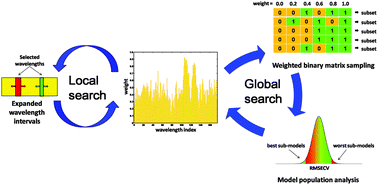
In this study, a new algorithm for wavelength interval selection, known as interval variable iterative space shrinkage approach (iVISSA), is proposed based on the VISSA algorithm. It combines global and local searches to iteratively and intelligently optimize the locations, widths and combinations of the spectral intervals. In the global search procedure, it inherits the merit of soft shrinkage from VISSA to search the locations and combinations of informative wavelengths, whereas in the local search procedure, it utilizes the information of continuity in spectroscopic data to determine the widths of wavelength intervals. The global and local search procedures are carried out alternatively to realize wavelength interval selection. This method was tested using three near infrared (NIR) datasets. Some high-performing wavelength selection methods, such as synergy interval partial least squares (siPLS), moving window partial least squares (MW-PLS), competitive adaptive reweighted sampling (CARS), genetic algorithm PLS (GA-PLS) and interval random frog (iRF), were used for comparison. The results show that the proposed method is very promising with good results both on prediction capability and stability. The MATLAB codes for implementing iVISSA are freely available on the website: http://www.mathworks.com/matlabcentral/fileexchange/49028-ivissa.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...