Switching of electrochemical characteristics of redox protein upon specific biomolecular interactions†
Abstract
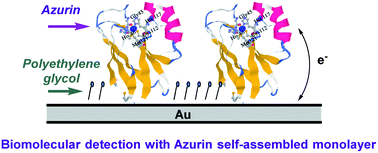
Detection of specific protein analytes is a technique widely used in disease diagnosis. Central to this approach is the fabrication of a sensing platform displaying a functional recognition element specific for the analyte targeted for detection. The most commonly utilised type of recognition element used for this purpose are antibodies. However direct generation of surfaces with high functional binding activity when using antibodies frequently presents a challenge, due to the conformational changes undergone by these molecules when physisorbed on a solid surface and/or variable activity when immobilized by covalent coupling techniques. Here, we present a novel label-free protein sensing platform based on a simplified and standardized immobilization process. The platform consists of self-assembled redox protein; Azurin (Az), that acts as scaffold, while sensing specificity is achieved through receptors that are coupled with chemical groups available on the surface of the Az protein. The redox activity of the Az within the sensing surface enables a label-free electrochemical detection method that can be readily miniaturized. We have observed a significant change in the electrochemical characteristics of the assay, upon a specific molecular interaction. A corresponding new model is also developed that can aid the future development of redox based bio-sensing techniques.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...