Room-temperature sensor based on surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy
Abstract
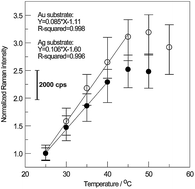
As reported in the literature, several factors, such as scattering cross sections, polarisability and wavelength suitability, contribute to increased SERS enhancement. In general, the advantage of surface-enhanced Raman scattering (SERS)-active Ag nanoparticles (NPs) is their higher SERS enhancement over Au NPs because the molar extinction coefficient of the Ag NPs is the highest of its kind among metals. Nevertheless, the corresponding SERS-active hot spots on Au are of inherently greater stability than on Ag. In this work, innovative temperature sensors based on SERS-active Au and Ag substrates prepared by sonoelectrochemical deposition–dissolution cycles (SEDDCs) are first reported. The SERS intensity of the model probe molecules of Rhodamine 6G (R6G) adsorbed on a SERS-active Ag substrate is monotonically increased from 25 to 50 °C. Moreover, this temperature-dependent intensity is linear with a slope of ca. 430 cps per °C between 25 to 45 °C. In addition, the reversibility and reusability of the developed temperature sensors are evaluated after the R6G-adsorbed sensors are alternately exposed to the temperatures of 25 and 45 °C in a sealed chamber. After every five cycles, the SERS spectra of treated substrates were recorded and compared with those of the as-prepared substrates. Experimental results indicate that SERS enhancement capability is mostly reversible based on 90% intensity of the Raman signal being maintained for the SERS-active Au substrate after 25 cycles (only 15 cycles for the Ag substrate).

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...