Microfluidic passive permeability assay using nanoliter droplet interface lipid bilayers†
Abstract
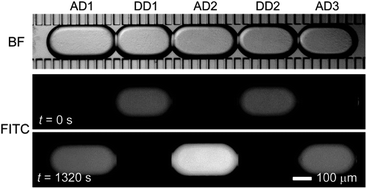
Membrane permeability assays play an important role in assessing drug transport activities across biological membranes. However, in conventional parallel artificial membrane permeability assays (PAMPA), the membrane model used is dissimilar to biological membranes physically and chemically. Here, we describe a microfluidic passive permeability assay using droplet interface bilayers (DIBs). In a microfluidic network, nanoliter-sized donor and acceptor aqueous droplets are alternately formed in cross-flowing oil containing phospholipids. Subsequently, selective removal of oil through hydrophobic pseudo-porous sidewalls induces the contact of the lipid monolayers, creating arrayed planar DIBs between the donor and acceptor droplets. Permeation of fluorescein from the donor to the acceptor droplets was fluorometrically measured. From the measured data and a simple diffusion model we calculated the effective permeabilities of 5.1 × 10−6 cm s−1, 60.0 × 10−6 cm s−1, and 87.6 × 10−6 cm s−1 with donor droplets at pH values of 7.5, 6.4 and 5.4, respectively. The intrinsic permeabilities of specific monoanionic and neutral fluorescein species were obtained similarly. We also measured the permeation of caffeine in 10 min using UV microspectroscopy, obtaining a permeability of 20.8 × 10−6 cm s−1. With the small solution volumes, short measurement time, and ability to measure a wide range of compounds, this device has considerable potential as a platform for high-throughput drug permeability assays.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...