Polydopamine-based molecular imprinting on silica-modified magnetic nanoparticles for recognition and separation of bovine hemoglobin†
Abstract
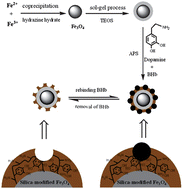
Surface molecular imprinting, especially on the surface of silica-modified magnetic nanoparticles, has been proposed as a promising strategy for protein recognition and separation. Inspired by the self-polymerization of dopamine, we synthesized a polydopamine-based molecular imprinted film coating on silica–Fe3O4 nanoparticles for recognition and separation of bovine hemoglobin (BHb). Magnetic molecularly imprinted nanoparticles (about 860 nm) possess a core–shell structure. Magnetic molecularly imprinted nanoparticles (MMIP) show a relatively high adsorption capacity (4.65 ± 0.38 mg g−1) and excellent selectivity towards BHb with a separation factor of 2.19. MMIP with high saturation magnetization (10.33 emu g−1) makes it easy to separate the target protein from solution by an external magnetic field. After three continuous adsorption and elution processes, the adsorption capacity of MMIP remained at 4.30 mg g−1. Our results suggest that MMIPs are suitable for the removal of high abundance of protein and the enrichment of low abundance of protein in proteomics.
- This article is part of the themed collection: 2013's Top 25 most read Analyst articles

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...