CTAB-capped Mn-doped ZnS quantum dots and label-free aptamer for room-temperature phosphorescence detection of mercury ions†
Abstract
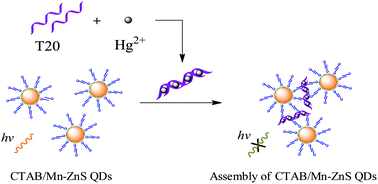
A new room-temperature phosphorescence (RTP) mercury ions sensor has been developed based on cetyltrimethylammonium bromide-capped Mn-doped ZnS

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...