A novel molecularly imprinted electrochemiluminescence sensor for isoniazid detection
Abstract
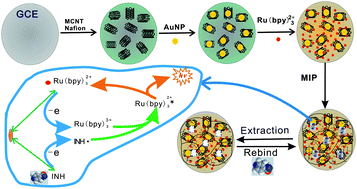
Based on Ru(bpy)32+-Au nanoparticles decorated multi-walled carbon nanotubes composites and a molecularly imprinted polymer (MIP), we propose a novel molecularly imprinted electrochemiluminescence (ECL) sensor to selectively determine isoniazid (INH). The MIP is synthesized through electrochemical copolymerization of acrylamide and N,N′-methylene diacrylamide in the presence of INH template molecules. The enhanced ECL intensity is linear in the range of 0.1 to 110 μg cm−3 and the detection limit is 0.08 μg cm−3 (3σ) INH with relative standard deviation 3.8% (n = 6) for 8 μg cm−3. As a result, the sensor has been successfully applied to the determination of INH in human urine and pharmaceutical samples. Moreover, the possible ECL mechanism is discussed.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...