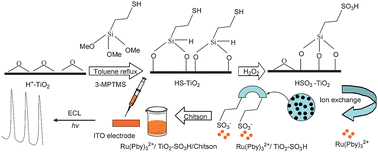
A novel Ruthenium(II) tris(bipyridine)-based solid-state electrochemiluminescence (ECL) sensor was developed in this paper. The sensor was fabricated by immobilising tris(2,2′-bipyridyl) ruthenium(II) (Ru(bpy)32+) in sulfonic-functionalised porous titania (TiO2–SO3H) nanoparticlesvia an ion exchange strategy, followed by employing environment friendly and stable biopolymer chitosan (CHIT) to entrap Ru(bpy)32+/TiO2–SO3H onto the ITO electrode. The prepared ECL sensor exhibited excellent ECL behaviors and a wide linear range from 7.5 × 10−9 to 2.5 × 10−3 M (R = 0.98) with a detection limit of 1.67 × 10−10 M (S/N = 3) towards 2-(dibutylamino)-ethanol (DBAE) detection. In addition, it had good reproducibility, and the relative average deviation was 0.95% of ECL intensity-time curve under continuous potential scanning for 34 cycles. It also had good long-term stability for the DBAE detection. After being used in three weeks, the sensor was able to keep over 80% activity towards 2.5 × 10−4 M of DBAE. Fabrication of the ECL sensor by this method is simple and easy, and hence has potential applications in ECL analysis and detection.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...