Raman spectroscopic monitoring of droplet polymerization in a microfluidic device†
Abstract
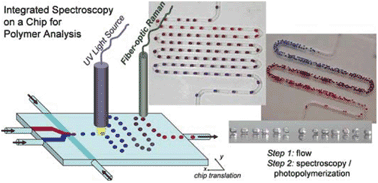
Microfluidic methodologies are becoming increasingly important for rapid formulation and screening of materials, and development of analytical tools for multiple sample screening is a critical step in achieving a combinatorial ‘lab on a chip’ approach. This work demonstrates the application of ![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) C stretching vibration at 1605 cm−1. Raman data allowed accurate measurement of the decrease in double bond conversion as a function of increasing crosslinker concentration. The results from the research demonstrate that
C stretching vibration at 1605 cm−1. Raman data allowed accurate measurement of the decrease in double bond conversion as a function of increasing crosslinker concentration. The results from the research demonstrate that

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...