Anthracene-functionalized dipolar glass copolymers as precursors for high-dielectric single-chain nanoparticles
Abstract
Dipolar glass copolymers (DGCs) incorporating 9-anthrylmethyl methacrylate (ANMA) with dipolar monomers 2-(methylsulfonyl)ethyl methacrylate (SO2MA) and 2-cyanoethyl methacrylate (CNMA) were synthesized via RAFT polymerization to develop high-performance dielectric materials with photo-responsive capabilities. Structural and spectroscopic analyses confirmed successful copolymer formation and anthracene incorporation, enabling ultraviolet (UV)-triggered functionalities. Thermal characterization revealed a significant increase in glass transition temperature (ΔTg ≈ +28 °C) compared to their homopolymer counterparts, despite a moderate reduction in thermal stability. Dielectric measurements demonstrated high permittivity 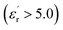 and low loss factors across a broad temperature range, with distinct γ, β, and α relaxation processes identified. Upon UV irradiation, anthracene photodimerization enabled efficient intramolecular cross-linking under dilute, oxygen-free conditions, leading to the formation of discrete single-chain nanoparticles (SCNPs) as confirmed by combined UV-visible spectroscopy, size-exclusion chromatography, and dynamic light scattering analyses. We explore, for the first time, the use of programmable nanoscale architectures to develop a new generation of single-chain high-dielectric nanomaterials. These materials exhibit high permittivity, relatively low dielectric losses, and suitable thermal properties in terms of glass transition temperature. Our results show that the localized environment and the reduction of long-range entanglements, arising from the collapse of linear DGC precursors into single-chain nanoparticles, do not significantly alter the dielectric response of these entities. As a result, they provide efficient dielectric materials with potential applications in energy storage, flexible electronics, sensors, and smart materials.
and low loss factors across a broad temperature range, with distinct γ, β, and α relaxation processes identified. Upon UV irradiation, anthracene photodimerization enabled efficient intramolecular cross-linking under dilute, oxygen-free conditions, leading to the formation of discrete single-chain nanoparticles (SCNPs) as confirmed by combined UV-visible spectroscopy, size-exclusion chromatography, and dynamic light scattering analyses. We explore, for the first time, the use of programmable nanoscale architectures to develop a new generation of single-chain high-dielectric nanomaterials. These materials exhibit high permittivity, relatively low dielectric losses, and suitable thermal properties in terms of glass transition temperature. Our results show that the localized environment and the reduction of long-range entanglements, arising from the collapse of linear DGC precursors into single-chain nanoparticles, do not significantly alter the dielectric response of these entities. As a result, they provide efficient dielectric materials with potential applications in energy storage, flexible electronics, sensors, and smart materials.



 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...