Electronic properties of ThC− and ThC
Abstract
The present study investigates the properties of low-lying states of ThC− and ThC using correlated wave function theories. To this end, we employed multireference calculations and various coupled-cluster approaches in combination with large correlation-consistent basis sets. These methods were applied to examine potential energy curves (PECs), electron configurations, energetics, spectroscopic constants, and spin–orbit coupling effects for 9 states of ThC− and 18 states of ThC. The ground states of ThC− and ThC were identified as single-reference 2Σ+1/2(I) and 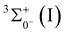 , respectively. Electron detachment from the 7s orbital of the Th center in ThC− [2Σ+(I); 1σ22σ13σ21π4] yields ThC [3Σ+(I); 1σ22σ13σ11π4]. The calculated adiabatic detachment energy (ADE) and vertical detachment energy (VDE) for this process are 1.591 and 1.604 eV, respectively. Furthermore, the dissociation energy (D0) of ThC [
, respectively. Electron detachment from the 7s orbital of the Th center in ThC− [2Σ+(I); 1σ22σ13σ21π4] yields ThC [3Σ+(I); 1σ22σ13σ11π4]. The calculated adiabatic detachment energy (ADE) and vertical detachment energy (VDE) for this process are 1.591 and 1.604 eV, respectively. Furthermore, the dissociation energy (D0) of ThC [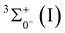 ] is predicted to be 5.099 eV. The standard enthalpy of formation,
] is predicted to be 5.099 eV. The standard enthalpy of formation, 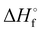 (298 K), of ThC is estimated to be 822.52 ± 6 kJ mol−1.
(298 K), of ThC is estimated to be 822.52 ± 6 kJ mol−1.



 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...