Crystal engineering of nickel(ii) coordination networks sustained by aliphatic dicarboxylate linker ligands
Abstract
Aliphatic dicarboxylate linker ligands are relatively understudied in the field of coordination networks (CNs) compared to their aromatic counterparts. Herein, we report the synthesis and characterisation of three nickel(II) CNs comprised of mixed ditopic linkers, a linear ditopic imidazolyl ligand and three aliphatic dicarboxylates: [Ni(glu)(bimbz)], sql-glu-Ni, [Ni(adi)(bimbz)(H2O)2], sql-adi-Ni, and [Ni(muc)(bimbz)(H2O)]·H2O, dia-muc-Ni (bimbz = 1,4-bis-(1H-imidazol-1-yl)benzene, glu = glutaric acid, adi = adipic acid, muc = trans, trans-muconic acid). Single crystal X-ray diffraction studies reveal that this family of CNs is comprised from nickel-based octahedral 4-connected nodes linked through nickel-carboxylate and nickel-imidazole coordination bonds. The resulting structures can be described as non-interpenetrated square lattice, sql, (sql-glu-Ni and sql-adi-Ni) or 5-fold interpenetrated diamondoid, dia, (dia-muc-Ni) topology networks. A Cambridge Structural Database (CSD) mining study was conducted to evaluate the effect of node composition and structure on topology in 222 archived CNs of general formula [MLL′], [MLL′(H2O)], [MLL′(H2O)2], [M2L2L′] (= “pillared paddlewheel”) and 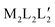 (= “double-walled nets”) where L = aliphatic dicarboxylate linker and L′ = linear ditopic N-donor linker. In terms of prevalence, sql, sql, neb, rob and pcu, respectively, were found to be the most common topologies for each of these compositions. These statistics suggest that aliphatic dicarboxylate linkers can have a profound and consistent effect on the resulting topology for certain node compositions. This is especially the case for “pillared paddlewheel” nets, which favour rob topology over the pcu or “DMOF” topology that dominates for rigid linkers.
(= “double-walled nets”) where L = aliphatic dicarboxylate linker and L′ = linear ditopic N-donor linker. In terms of prevalence, sql, sql, neb, rob and pcu, respectively, were found to be the most common topologies for each of these compositions. These statistics suggest that aliphatic dicarboxylate linkers can have a profound and consistent effect on the resulting topology for certain node compositions. This is especially the case for “pillared paddlewheel” nets, which favour rob topology over the pcu or “DMOF” topology that dominates for rigid linkers.



 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...