Fe-doped α-MnO2/rGO cathode material for zinc ion batteries with long lifespan and high areal capacity†
Abstract
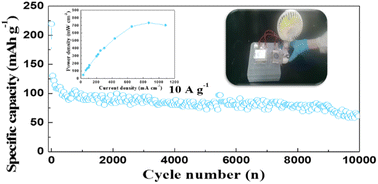
Currently, research interest in aqueous zinc ion batteries (ZIBs) has surged throughout the world owing to their merits of high theoretical energy density, high safety and low cost. However, the lack of suitable cathode materials with high energy density and cycling stability has severely restricted the further development and practical application of ZIBs. Herein, we propose a facile Fe heteroatom doping and rGO external coating modification strategy for preparing an Fe-doped α-MnO2/rGO cathode material with excellent kinetic performance and structural stability for ZIBs. The introduction of heterogeneous Fe increased carrier concentration and induced Mn-defects in the α-MnO2 lattice, which not only improved electronic conductivity, but also attenuated electrostatic interactions during the process of Zn2+ ion insertion/extraction. Furthermore, the coated rGO layer with a thickness of about 4 nm significantly suppressed the dissolution of Mn2+ ions and volume expansion during cycles. Consequently, it delivered a high specific capacity of 167.7 mA h g−1 at 1 A g−1 after 2000 cycles and an excellent rate capacity of 62.5 mA h g−1 at 15 A g−1. Encouragingly, an imposing areal capacity of 32.8 mA h cm−2 and a specific capacity of 164.2 mA h g−1 were observed at 0.05C (1C = 308 mA h g−1) for a highly active material loading of 200 mg cm−2.
- This article is part of the themed collection: 2024 Journal of Materials Chemistry A HOT Papers


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...