The balancing act between high electronic and low ionic transport influenced by perovskite grain boundaries†
Abstract
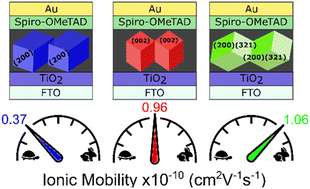
A better understanding of the materials' fundamental physical processes is necessary to push hybrid perovskite photovoltaic devices towards their theoretical limits. The role of the perovskite grain boundaries is essential to optimise the system thoroughly. The influence of the perovskite grain size and crystal orientation on physical properties and their resulting photovoltaic performance is examined. We develop a novel, straightforward synthesis approach that yields crystals of a similar size but allows the tuning of their orientation to either the (200) or (002) facet alignment parallel to the substrate by manipulating dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) and tetrahydrothiophene-1-oxide (THTO) ratios. This decouples crystal orientation from grain size, allowing the study of charge carrier mobility, found to be improved with larger grain sizes, highlighting the importance of minimising crystal disorder to achieve efficient devices. However, devices incorporating crystals with the (200) facet exhibit an s-shape in the current density–voltage curve when standard scan rates are used, which typically signals an energetic interfacial barrier. Using the drift-diffusion simulations, we attribute this to slower-moving ions (mobility of 0.37 × 10−10 cm2 V−1 s−1) in combination with a lower density of mobile ions. This counterintuitive result highlights that reducing ion migration does not necessarily minimise hysteresis.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...