Levofloxacin degradation in a heterogeneous electro-Fenton system with an FeOCl/MoS2 composite catalyst
Abstract
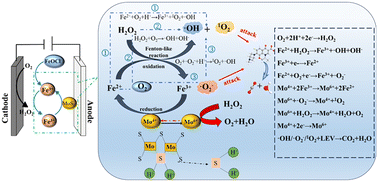
To overcome the drawbacks of traditional electro-Fenton (EF) technology, such as acidic conditions (pH 3–4) and the extensive leaching of Fe ions, FeOCl/MoS2 composites were synthesized through a simple calcination method. Furthermore, a heterogeneous electro-Fenton system was equipped with nickel foam (NF) as the anode and Pt foil as the cathode, effectively removing levofloxacin (LEV). Under optimal experimental conditions (FeOCl/MoS2 0.15 g L−1, initial pH = 3, applied voltage 2.5 V, and LEV concentration 10 mg L−1), the removal rate of LEV reached 95.2% and the mineralization was 75.39% in 160 min. By measuring the changes of the Fe ions in three different EF systems EF-FeOCl/MoS2, EF-FeOCl, and EF-FeSO4, it was found that the addition of Mo4+ accelerated the conversion between Fe3+ and Fe2+ and effectively reduced the formation of Fe sludge. The EF-FeOCl/MoS2 process exhibited degradation rates of over 80% for LEV in a wide pH range (3–9), thereby overcoming the limitations of traditional electro-Fenton acidic conditions. Besides, the degradation intermediates were studied, and the pathways and mechanisms of the EF-FeOCl/MoS2 system catalytic degradation of LEV were proposed. The prepared FeOCl/MoS2 catalyst in this study provides a feasible approach for rapidly removing contaminants in wastewater.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...