The impact of thickness-related grain boundary migration on hole concentration and mobility of p-type transparent conducting CuI films
Abstract
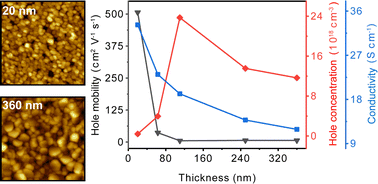
CuI films present promising optoelectronic properties for transparent conductors. However, the high hole concentration in CuI films hinders the controllable modulation of hole mobility, limiting their application in low-dimensional thin-film transistors. In this study, CuI films were prepared through a Cu film iodination method at room temperature, and a systematic investigation was conducted on the modulation of hole concentration and mobility with varying film thickness. The films exhibited a zinc blende structure (γ-phase) with increasing grain size as the thickness increased. The transmittance and optical bandgap of the films decreased with increasing thickness. The correlation of vacancy concentration with changing film thickness was analyzed through photoluminescence spectroscopy, revealing the influence of grain boundary migration on vacancy formation. The reduction in film thickness diminishes the migration of CuI grain boundaries, consequently reducing the probability of Cu vacancy and I vacancy formation, resulting in diminished hole concentration and enhanced hole mobility and film conductivity. The film with a thickness of 20 nm demonstrated optimal performance, with a transmittance of 90%, hole concentration of 4.09 × 1017 cm−3, hole mobility of 506.50 cm2 V−1 s−1, and conductivity of 33.19 S cm−1. This work deepens the understanding of hole transport such as hole concentration and mobility modulation in CuI films, highlighting the importance of controlling grain boundary migration during the film growth process.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...