Protection against myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury in mice by 3-caffeoylquinic acid isomers isolated from Saxifraga tangutica†
Abstract
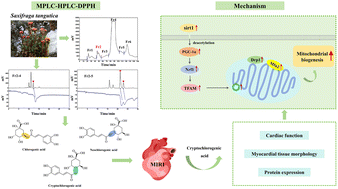
The development of ischemic heart disease (IHD) involves a variety of pathophysiological responses, such as mitochondrial dysfunction. Many compounds with antioxidant activity isolated from natural products have been shown to have significant effects on the prevention and treatment of cardiovascular diseases. However, little is known about the palliative effects of 3-caffeoylquinic acid isomers isolated from Saxifraga tangutica (S. tangutica) on myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury (MIRI). Three isomers of 3-caffeoylquinic acid were isolated from S. tangutica and identified as neochlorogenic acid (Fr2-4-1-1, 18.5 mg), chlorogenic acid (Fr2-5-1-1, 81.7 mg) and cryptochlorogenic acid (Fr2-5-2-1, 15.0 mg) using medium-pressure liquid chromatography-high-pressure two-dimensional liquid chromatography. An in vitro DPPH assay showed that cryptochlorogenic acid (CCGA), neochlorogenic acid (NCGA) and chlorogenic acid (CGA) (in order of activity from strongest to weakest) possessed superior antioxidant activity. Langendorff's in vitro model was utilized to explore the protective effects of 3 caffeoylquinic acid isomers against MIRI. The ex vivo MIRI assay demonstrated that CCGA significantly improved hemodynamic function (P < 0.05), hemodynamic function-related indices (LVDP, RPP, +dP/dt and −dP/dt), and cell morphology in I/R myocardium tissues. In addition, the results of western blot analysis showed that mitochondrial biogenesis was significantly increased in I/R myocardial tissues after treatment with CCGA. In contrast, the activities of CGA and NCGA were lower. This is the first demonstration of efficient preparative isolation of 3-caffeoylquinic acid isomers (CGA, NCGA and CCGA) from S. tangutica. CCGA may be a promising approach for the treatment of cardiac I/R injury, especially for the regulation of mitochondrial biogenesis after MIRI.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...