Optimization and pathway study on destruction of the spent extraction solvent in supercritical water
Abstract
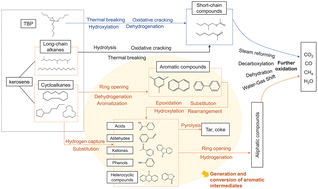
Sustainable management of spent extraction solvents (SES) is paramount in the nuclear industry. This study delves into the optimization and oxidation pathways of treating these solvents using supercritical water oxidation (SCWO). Response surface methodology (RSM) has been employed to optimize key operating variables, that is, temperature, residence time and oxidant concentration, producing a highly accurate quadratic polynomial model. The results showed that the total organic carbon (TOC) removal could reach up to 99.25% under 549 °C, 67.7 s and with an oxidation coefficient of 274.3%. Product analysis of the effluent via GC-MS/FTIR/GC revealed the pivotal role of ketones and aldehydes as major intermediates. This study proposes potential chemical pathways for the destruction of these solvents, providing invaluable insights for process intensification. In conclusion, this study underscores the potential of SCWO as an efficient and sustainable solution for disposing of SES in the nuclear industry.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...