Engineering peptide-modified alginate-based bioinks with cell-adhesive properties for biofabrication†
Abstract
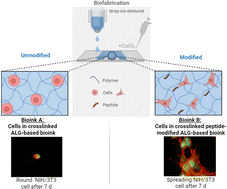
Alginate (ALG) and its oxidised form alginate-dialdehyde (ADA) are highly attractive materials for hydrogels used in 3D bioprinting as well as drop-on-demand (DoD) approaches. However, both polymers need to be modified using cell-adhesive peptide sequences, to obtain bioinks exhibiting promising cell-material interactions. Our study explores the modification of ALG- and ADA-based bioinks with the adhesive peptides YIGSR (derived from laminin), RRETEWA (derived from fibronectin) and IKVAV (derived from laminin) for 3D bioprinting. Two coupling methods, carbodiimide and Schiff base reactions, were employed to modify the polymers with peptides. Analytical techniques, including FTIR and NMR were used to assess the chemical composition, revealing challenges in confirming the presence of peptides. The modified bioinks exhibited decreased stability, viscosity, and stiffness, particularly-ADA-based bioinks in contrast to ALG. Sterile hydrogel capsules or droplets were produced using a manual manufacturing process and DoD printing. NIH/3T3 cell spreading analysis showed enhanced cell spreading in carbodiimide-modified ADA, Schiff base-modified ADA, and PEG-Mal-modified ADA. The carbodiimide coupling of peptides worked for ADA, however the same was not observed for ALG. Finally, a novel mixture of all used peptides was evaluated regarding synergistic effects on cell spreading which was found to be effective, showing higher aspect ratios compared to the single peptide coupled hydrogels in all cases. The study suggests potential applications of these modified bioinks in 3D bioprinting approaches and highlights the importance of peptide selection as well as their combination for improved cell–material interactions.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...