Ilmenite-derived titanic acid species: exploring their outstanding light-independent antibacterial activity
Abstract
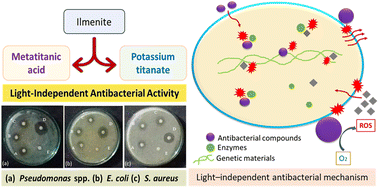
The emergence of resistance in detrimental pathogenic bacteria towards well-recognized antibiotics has greatly impacted global medicine, consequently exploring potent antibacterial compounds is becoming a potential area of research. Although photocatalytic metal oxides have been extensively explored in this regard, their applicability is diminished due to the requirement of photon energy. Therefore, in our study, we explored the light-independent antibacterial effect of two unexplored titanium species, known as metatitanic acid (MTA) and potassium titanate, against Staphylococcus aureus, Escherichia coli, and Pseudomonas spp. using the disk diffusion method in Luria–Bertani agar medium, where the well-known antibiotic, gentamicin, was used as the positive control. These two titanium compounds were readily synthesized through a novel process which was originally developed for the extraction of TiO2 from ilmenite. The synthesized MTA was characterized using FT-IR, Raman spectroscopy, XRD, TGA, UV-visible spectroscopy, and SEM. According to our findings, both MTA and potassium titanate exhibited superior light-independent antibacterial properties, where for some concentrations, the effect was even greater than gentamicin. However, nano-TiO2 totally failed as an antibacterial compound against the tested three strains under dark conditions.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...