Natural transaminase fusions for biocatalysis†
Abstract
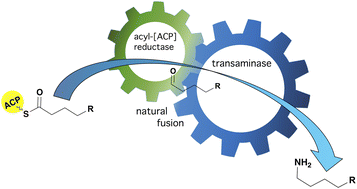
Biocatalytic approaches are used widely for the synthesis of amines from abundant or low cost starting materials. This is a fast-developing field where novel enzymes and enzyme combinations emerge quickly to enable the production of new and complex compounds. Natural multifunctional enzymes represent a part of multi-step biosynthetic pathways that ensure a one-way flux of reactants. In vivo, they confer a selective advantage via increased reaction rates and chemical stability or prevention of toxicity from reactive intermediates. Here we report the identification and analysis of a natural transaminase fusion, PP_2782, from Pseudomonas putida KT2440, as well as three of its thermophilic homologs from Thermaerobacter marianensis, Thermaerobacter subterraneus, and Thermincola ferriacetica. Both the fusions and their truncated transaminase-only derivatives showed good activity with unsubstituted aliphatic and aromatic aldehydes and amines, as well as with a range of α-keto acids, and L-alanine, L-glutamate, and L-glutamine. Through structural similarity, the fused domain was recognised as the acyl-[acyl-carrier-protein] reductase that affects reductive chain release. These natural transaminase fusions could have a great potential for industrial applications.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...