Quinoline–sulfonamides as a multi-targeting neurotherapeutic for cognitive decline: in vitro, in silico studies and ADME evaluation of monoamine oxidases and cholinesterases inhibitors†
Abstract
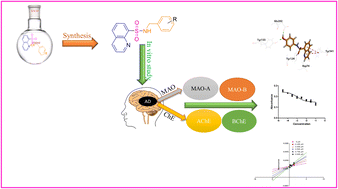
Alzheimer's disease (AD) is a multifactorial irreversible neurological disorder with multiple enzymes involved. In the treatment of AD, multifunctional agents targeting cholinesterase (ChE) and monoamine oxidase (MAO) inhibitors have shown promising results. Herein, a series of novel quinoline–sulfonamides (a1–18) were designed and synthesized as a dual inhibitor of MAOs and ChEs. The in vitro results showed that compounds a5, a12, a11, and a6 exhibited the most potent compounds against specific enzymes. They had IC50 value 0.59 ± 0.04 for MAO-A, 0.47 ± 0.03 for MAO-B, 0.58 ± 0.05 for BChE and 1.10 ± 0.77 for AChE μM respectively. Furthermore, kinetic studies revealed that these compounds are competitive. Molecular docking studies enhanced the understanding of the in silico component, unveiling critical interactions, specifically the hydrogen bonding interaction, π–π, π–alkyl, π–amid and π–sulfur interactions between the ligand and enzymes. These findings suggest that compounds a5, a6, a11, a12, a15, and a18 may be potent multifunctional candidates for AD treatment.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...