Disruption of lipid metabolism to induce ferroptosis using multifunctional fibrate-Pt(iv) prodrugs for cancer treatment†
Abstract
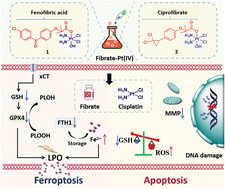
Ferroptosis is an iron-mediated regulated cell death initiated by excessive membrane lipid peroxide accumulation. The intimate interplay between ferroptosis and lipid metabolism suggests that modulating lipid metabolism and activating ferroptosis may represent a broader cancer therapeutic space. Herein, two fibrate lipid-modulating agents, fenofibric acid and ciprofibrate, were employed to functionalize the clinical drug cisplatin through a Pt(IV) prodrug strategy, affording four fibrate-Pt(IV) anticancer prodrugs, compounds 1–4, with prominent anticancer activity and ferroptosis induction. The representative compounds, 1 and 3, exhibited antiproliferative activity up to 140- and 90-fold greater than cisplatin, respectively. Our data demonstrated that fibrate-Pt(IV) prodrugs accumulated in A549 cells much higher than cisplatin, followed by a dramatic decrease in intracellular lipid content, elevated reactive oxygen species (ROS) levels, disruption of the mitochondrial transmembrane potential, and remarkable proliferation inhibition. Moreover, our results revealed that fibrate-Pt(IV) prodrugs not only induced DNA damage, apoptosis, and cell cycle arrest, but also led to increases in lipid peroxides, ferrous ions, and malondialdehyde (MDA), as well as a decrease in glutathione, which triggers ferroptosis by suppressing the system Xc−/GSH/GPX4 antioxidant defense axis and stimulation of the iron axis. Our results emphasize that combining lipid metabolism regulation with ferroptosis to develop new platinum-based anticancer agents can produce excellent multi-action anticancer activities, which may represent a promising cancer treatment modality.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...