Advances of cassava starch-based composites in novel and conventional drug delivery systems: a state-of-the-art review
Abstract
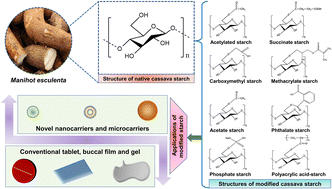
Starch has emerged as a new attractive biopolymer for use in pharmaceutical applications, owing to its distinctive physical, chemical and functional properties. This biopolymer has several potential advantages: it is biocompatible, low cost, non-toxic and easily isolated from plant sources. In the pharmaceutical field, starch is used as a raw material for developing various drug delivery platforms. Generally, cassava starch (tapioca) is obtained from the swollen roots of the perennial shrub Manihot esculenta and it contains a low amount of amylose in contrast to other varieties of starches. Because of this reason, cassava starch exhibits various prime benefits, including a low gelatinization temperature, higher swelling power and a relatively high viscosity paste, making it a preferable excipient for pharmaceutical applications. However, cassava starches in their native form are not effective for many applications because of their inefficiency in handling various processing requirements like high temperature and diverse pH. Their applicability can be enhanced by starch modification. These functional starches have demonstrated outstanding prospects as primary excipients in many pharmaceutical formulations. In this article, we discuss the potential application of cassava starches in the pharmaceutical and biomedical fields, along with the toxicity assessment of modified cassava starches.
- This article is part of the themed collection: RSC Pharmaceutics 2024 Hot Articles


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...